Yearbook 2013
El Salvador. The ceasefire between El Salvador’s largest crime leagues, M18 and Mara Salvatrucha, which was closed in March 2012, seemed largely to hold during the year. For example, the number of homicides in the country fell by 18%. However, a certain increase in the violence was noted in July and August, and Justice Minister Ricardo Perdomo attributed it to purges in the gang, among other things. within M18 where a faction did not accept the cease-fire. In September, police conducted a raid on the league in the capital San Salvador and some of its suburbs, leading to the arrest of 90 people.
According to Countryaah, Venezuela’s new president Nicolás Maduro in March accused El Salvador’s right-wing opposition party ARENA (Alianza Republicana Nacionalista) of being involved in a murder plot against him. Similar accusations had been made by him before, i.e. against a couple of US diplomats, but El Salvador President Mauricio Funes said he considered Maduro to be a credible person and that it could thus lie somewhat in the allegations. Representatives of ARENA, in turn, argued that there were simply lies on Maduro’s side to bolster his opinion in Venezuela, and that Funes had his own domestic policy goals and used Maduro’s statement to discredit ARENA for the March 2014 elections.
El Salvador
Isthmian Central American State. It borders to the East and N with Honduras, to the West with Guatemala, while to the South it overlooks the Pacific Ocean.
Physical characteristics
The territory, almost rectangular in shape, is made up of an elevated internal area and a flat coastline bordered by lagoons. The first consists of a plateau about 600 m high engraved by numerous watercourses and from which various volcanic cones rise, some more than 1000 m high, partly still active; volcanism is associated with a high seismicity which has often given rise to catastrophic episodes. The main river is the Río Lempa, whose valley occupies a structural depression. The climate is hot and humid (average annual temperature 26-28 ° C) and often unhealthy in the coastal region, mitigated by the altitude and generally healthy in inland areas; rainfall is abundant everywhere, but especially on the coast, where it allows for the development of rainforests.
Population
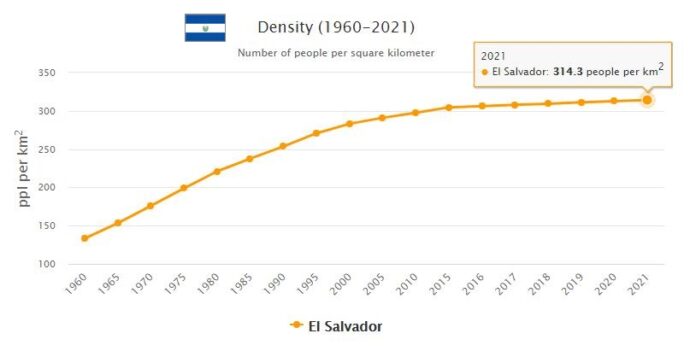
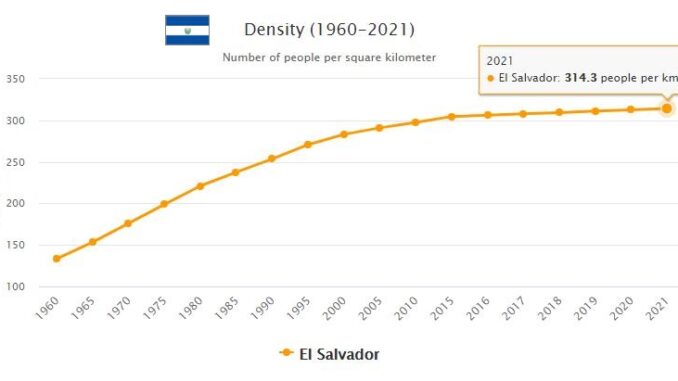
The El Salvador is the most densely populated among the countries of Isthmian America. The density reaches its maximum values in the area around the capital and gradually decreases towards the periphery. The demographic increase is notable, mainly due to natural dynamics. The urbanization process is also growing, leading the urban population to represent 61% of the total (2009). Because of the conflicts that in the 1980s bloodied the country, the El Salvador was the scene of important migratory phenomena, with significant flows of refugees directed to the United States and neighboring countries. Mestizos (88.3%) clearly prevail over Amerindians (9.1%) and Creoles (1.6%). The major cities, all inland, are, in addition to the capital (which is by far the most important economic and cultural center), Santa Ana, San Miguel and Nueva San Salvador. In addition to Spanish, Amerindian languages are widely spoken; the clearly prevalent religion is the Catholic one.
Economic conditions
The economy of the El Salvador was heavily affected by the political tension and the troubled internal events that in the 1980s led the country to a long civil war. Furthermore, recurrent natural disasters strongly penalize agriculture, which occupies 19% of the active population (2009). The most important crop is that of coffee (the main export product), followed by sugar cane and cotton; corn, beans and rice are intended for internal consumption. Over 90% of farms are made up of very small funds (microfunds), which cover just 21% of the total area, and the rest of large estates occupied by the profitable plantations of export products. The forests, the surface of which, moreover, contracted strongly in the course of the 20th century, they supply precious woods (mahogany) and essences used in the pharmaceutical industry (the best known is the so-called balsam of Peru). ● The secondary sector contributes to the formation of GDP for 28.8% and employs 23% of the active population. Production, under the leadership of multinationals, has also developed in El Salvador, as in the rest of the countries of the area, around structures called maquiladoras, assembly companies of intermediate products imported at zero tariffs and subsequently re-exported as finished products. An important source of foreign currency are emigrant remittances and, above all, tourism, which, started after the end of the long civil conflict and favored bythe country’s natural beauties, represents an important opportunity for development. ● As regards foreign trade, the main trading partners are, for imports, the United States, Mexico, Guatemala and China; for exports, the United States, Guatemala, Honduras and Nicaragua. ● The El Salvador has a railway network of just under 300 km, a road network of 10,886 km (of which only 1/5 are asphalted) which includes a section of the Pan-American Highway, some active ports (especially La Unión and La Libertad, a stopover serving the capital) and an international airport.
San Salvador
San Salvador, capital of El Salvador; 561,400 residents (2012), including suburbs 2 million residents. San Salvador, located on the San Salvador volcano about 60 km from the Pacific coast, is an industrial, financial and commercial center with several universities. The city has road links with neighboring countries and Pacific ports as well as the international airport, Comalapa.
- According to AbbreviationFinder.org, San Salvador is the capital city of El Salvador. See acronyms and abbreviations related to this capital and other major cities within this country.
San Salvador, founded in the 1520s by Pedro de Alvarado, became the capital of the Central American Union in 1834 and in 1839 in El Salvador. The city was hit by severe earthquakes in 1854, 1873, 1917 and 1919. Throughout the 1980s, San Salvador was characterized by the civil war that reached the central parts of the city in the late 1989-90. After the end of the war in 1992, San Salvador has been hit by sharply increasing crime.